您现在的位置是: 首页 > 教育比较 教育比较
高考不定代词_高考不定代词真题
tamoadmin 2024-07-23 人已围观
简介1.高考英语词汇分类讲解:人称代词2.什么叫复合不定代词3.高考英语语法填空的技巧和方法4.英语中的代词是什么意思5.语法填空无提示词可以填不定代词吗6.高中英语语法知识点整理总结7.代词的固定搭配不定代词指人时用who,指物用that,既指人又指物,用that,这是初中学的,但是到了高中,人的很少考,老师也很少要求,指物的却经常考,老师也经常强调,准确的说应该是只能用that的情况考的多,只能用
1.高考英语词汇分类讲解:人称代词
2.什么叫复合不定代词
3.高考英语语法填空的技巧和方法
4.英语中的代词是什么意思
5.语法填空无提示词可以填不定代词吗
6.高中英语语法知识点整理总结
7.代词的固定搭配
不定代词指人时用who,指物用that,既指人又指物,用that,
这是初中学的,但是到了高中,人的很少考,老师也很少要求,指物的却经常考,老师也经常强调,准确的说应该是只能用that的情况考的多,只能用who的我还没考过。
高考英语词汇分类讲解:人称代词
《高中英语语法-定语从句》由英语我整理,更多请访问:s://.liuxue86/english/。本内容整理时间为05月12日,如有任何问题请联系我们。
定语从句
(一)定语从句一般由关系代词和关系副词引导
1、关系代词:who, whom, whose, which, that, as
2、关系副词:when, where, why
关系代词和关系副词必须位于从句之首,主句先行词之后,起着连接先行词和从句的作用, 同时在从句中又充当句子成分。
e.g. She is the girl who sings best of all.(关系代词who在从句中作主语)
The comrade with whom I came knows French.(whom在从句中作介词with的宾语)
3、关系代词和关系副词的用法:1)当先行词为人时用who 作主语,whom作宾语;2)当先行词为物或整个句子时用which ,可作主语或宾语;3)先行词为人、物时用that ,可作主语或宾语;4)whose用作定语,可指人或物;5)关系副词when(指时间,在定语从句中作时间状语,where(指地点,在定语从句中作地点状语),why(指原因,在定语从句中作原因状语)。
(二)限制性定语从句与非限制性定语从句
1、限制性定语从句:从句与主句关系密切,去掉从句,主句意义不完整,甚至不合逻辑。
e.g. I was the only person in our office who was invited.(去掉定语从句,意思就不完整)
2、非限制性定语从句:从句对先行词关系不密切,去掉定从句,意思仍然完整。形式上用逗号隔开,不能that用引导。
e.g. Tom's father, who is over sixty, still works hard day and night.(who引导非限制性定语从句,整个句子可分成两句来翻译)
(三)使用定语从句时特别注意的几个问题
1、that与which的区别。
1)用that而不用 which的情况:①先行词为不定代词all, anything, nothing, ?;②先行词有最高级修饰,有序数词修饰;③先行词有only, very, any等词修饰;④先行词既有人又有物时。
e.g. There is nothing that can prevent him from doing it. 没有什么能阻止他不干那件事。
The first place that they visited in Guilin was Elephant Trunk Hill. 在桂林他们所参观的第一个地方是象鼻山。
This is the best film that I he ever seen. 这部**是我看过的最好的一部。
Mr Smith is the only foreigner that he knows. 史密斯先生是他认识的唯一的外国人。
2)用which而不用 that的情况:①引导非限制性定语从句;②代表整个主句的意思;③介词 + 关系代词。
e.g. He had failed in the maths exam, which made his father very angry. 他数学考试没有及格,这使他的父亲很生气。
This is the room in which my father lived last year. 这是父亲去年居住过的房子。
3)as引导定语从句时的用法
①as引导限制性定语从句通常用于the same ? as, such ? as结构中。
e.g. I want the same shirt as my friend's. 我要一件跟我朋友一样的衬衫。
Such machines as are used in our workshop are made in China. 我们车间使用的这种机器是中国制造的。
②as引导非限制性定语从句既可放在主句之前,也可放在主句之后,用来修饰整个句子。通常用下列句型:as is known to all, as is said, as is reported, as is announced, as we all know, as I expect 等。
e.g. As I expected, he got the first place again in this mid-term examination. 正如我所预料的那样,他在这次期中考试中又获得了第一名。
3)as 引导非限制性定语从句时与which的区别
①当主句和从句语义一致时,用as;反之,用which来引导非限制性定语从句。
e.g. He made a long speech, as we expected.
He made a long speech, which was unexpected.
②当非限制定语从句为否定时,常用which引导。
e.g. Tom drinks a lot every day, which his wife doesn't like at all.
2. 关系代词在从句中作主语时,从句的谓语动词单数还是用复数应由先行词决定。
e.g. The man who lives downstairs speaks English fluently. 住在楼下的那个人英语说得很流利。
The students who are in Grade Three are going to climb the hill tomorrow.
3. 定语从句有时不直接紧靠先行词,中间由一个定语、状语或谓语隔开。
e.g. There is an expression in his eyes that I can't understand.
4. 引导定语从句的关系副词有时可以用"介词 + which"来代替。
e.g. October 1, 1949 was the day on which ( = when ) the People's Republic of China was founded.
5. 当定语从句中谓语动词是带介词或副词的固定短语动词时,短语动词的各个固定部分不要拆开。
e.g. The sick man whom she is looking after is her father.
6. 介词在关系代词前,只能用which和whom,且不能省略;介词在句尾,关系代词可有which, that, whom, 口语中也可用who,且可省略。
e.g. The man (whom/ who/ that) you were talking about has come to school.
练习、定语从句
一、把下列每对句子合并成含有定语从句的主从复合句:
1. The fan is on the desk. You want it.
2. The man is in the next room. He brought our textbooks here yesterday.
3. The magazine is mine. He has taken it away.
4. The students will not pass the exam . They don't study hard.
5. The woman is our geography teacher. You saw her in the park.
6. The letter is from my sister. I received it yesterday.
7. The play was wonderful. We saw it last night.
8. The train was late. It was going to Nanning.
9. The boy is my brother. He was here a minute ago.
10. The tree is quite tall. He is climbing it.
11. Here is the girl. Her brother works in this shop.
12. That's the child. We were looking at his drawing just now.
13. This is the boy. His sister is a famous singer.
14. I want to talk to the boys. Their homework hen't been handed in.
15. Is that the woman? Her daughter is in my class.
16. He used to live in a big house. In front of it grew many banana trees.
17. They passed a factory. At the back of the factory there were rice fields.
18. The soldier ran to the building. On the top of it flew a flag.
19. In the evening they arrived at a hill. At the foot of the hill there was a temple.
20. She came into a big room. In the middle of it stood a large table.
二、根据句子意思,在第一个空白处填入介词,在第二个填入关系代词whom或which:
1. The person ________ ________ I spoke just now is the manager that I told you about.
2. The pencil ________ ________ he was writing broke.
3. Wu Dong, ________ ________ I went to the concert, enjoyed it very much.
4. The two things ________ ________ Marx was not sure were the grammar and some of the idioms of English.
5. Her bag, ________ ________ she put all her books, has not been found.
6. The stories about the Long March, ________ ________ this is one example, are well written.
三、选择填空:
1. The man ____ visited our school yesterday is from London.
A. who B. which C. whom D. when
2. The woman ____ is talking to my mother is a friend of hers.
A. whose B. who C. whom D. which
3. Because of my poor memory, all ____ you told me has been forgotten.
A. that B. which C. what D. as
4. Do you remember those days ____ we spent along the seashore very hily?
A. when B. where C. which D. who
5. Tom did not take away the camera because it was just the same camera ____ he lost last week.
A. which B. that C. whom D. as
6. Those ____ want to go please sign their names here.
A. whom B. which C. who D. when
7. Where is the man ____ I met this morning?
A. when B. where C. which D. who
8. Who is the woman ____ is sweeping the floor over there?
A. who B. / C. that D. when
9. The man ____ you talked just now is a worker.
A. who B. whom C. to whom D. to who
10. The man ____ you are going to make friends is my father's neighbour.
A. with whom B. when C. to whom D. which
11. The doctor ____ is leing for Africa next month.
A. the nurse is talking to him B. whom the nurse is talking
C. the nurse is talking to D. who the nurse is talking
12. The man ____ around our school is from America.
A. which you showed B. you showed him C. you showed D. where you showed
13. He talked about a hero ____ no one had ever heard.
A. of whom B. from whom C. about that D. who
14. In fact the Swede did not understand the three questions ____ were asked in French.
A. where B. who C. in which D. which
15. He you read the book ____ I lent to you?
A. that B. whom C. when D. whose
16. Finally, the thief handed over everything ____ he had stolen to the police.
A. that B. which C. whatever D. all
17. The foreign guests, ____ were officials, were warmly welcomed at the airport.
A. most of them B. most of that C. most of whom D. most of those
18. This is the very letter ____came last night.
A. who B. which C. that D. as
19. I know only a little about this matter; you may ask ____ knows better than I.
A. whoever B. whomever C. anyone D. the one
20. This is the school ____ we visited three days ago.
A. where B. / C. when D. what
21. This is the factory ____ we worked a year ago.
A. where B. that C. which D. on which
22. Nearby were two canoes ____ they had come to the island.
A. which B. in which C. that D. /
23. Jack is pleased with ____ you he given him and all ____ you he told him.
A. that, what B. what, that C. which, what D. that, which
24. Do you work near the building ____ colour is yellow?
A. that B. which C. its D. whose
25. In the dark street, there wasn't a single person ____ she could turn for help.
A. whom B. who C. to whom D. form whom
26. Is this school ____ we visited three years ago?
A. the one B. which C. that D. where
27. Is this the school ____ we visited three years ago?
A. the one B. where C. in which D. /
28, How many students are there in your class ____ homes are in the country?
A. whose B. who C. whom D. which
29. Alice received an invitation from her boss, ____ came as a surprise.
A. it B. which C. that D. he
30. The train was crowded and I had to get into a carriage ____ already seven other people.
A. when there were B. which there were C. that there were D. where there were
31. I live in the house ____ windows face south.
A. which B. whose C. where D. in that
32. ---- What game is popular with them? ---- The ____ most is tennis.
A. game they like it B. game they like C. best game they like D. best game they like it
33. They stayed with me three weeks, ____ they drank all the wine I had.
A. which B. which time C. during which time D. during which
34. The room ____ Mr White lives is not very large.
A. that B. which C. where D. when
35. Don't forget the day ____ you were received into the Youth League.
A. when B. that C. at which D. where
36. I've finished writing the novel, ____ is to be published next month.
A. that B. what C. which D. when
37. He returned home safe and sound after a fierce battle, ____ was unexpected.
A. which B. as C. that D. it
38. ____ we is known to all, English is not very difficult to learn.
A. What B. As C. That D. Which
39. The old man had three sons, all of ____ died during World War Ⅱ.
A. whose B. that C. whom D. who
40. I he bought two pens, ____ write well.
A. none of which B. neither of which C. both of which D. all of which
41. Do you know the reason ____ she has changed her mind?
A. why B. which C. for that D. of which
42. He failed in the exam, ____ proves that he wasn't working hard enough.
A. which B. what C. it D. that
43. During the week ____ he tried to collect materials for his article.
A. following B. followed C. to follow D. that followed
44. ____ was expected, he succeeded in the exam.
A. It B. Which C. As D. That
45. He studied hard and later became a well-known writer, ____ his father expected.
A. that was what B. what was that C. and which was D. which was what
46. We should read such books ____ will make us better and wiser.
A. when B. as C. whose D. what
47. You must show my wife the same respect ____ you show me.
A. when B. as C. whose D. what
48. He is absent ____ is often the case.
A. what B. which C. who D. as
49. It is the first time ____ I he come to your city.
A. that B. which C. what D. when
50. Who ____ has the same idea as it will do it in this way.
A. who B. that C. whom D. which
51. I shall never forget those years ____ I lived in the country with the farmers, ____ has a great effect on my life.
A. that, which B. when, which C. which, that D. when, who
52. This is the only book ____ I can find.
A. that B. which C. it D. with which
53. I don't like ____ you speak to her.
A. the way B. the way in that C. the way which D. the way of which
54. That is one of those books that ____ worth reading.
A. is B. are C. has D. he
55. This is the only one of the students whose handwriting ____ the best.
A. is B. are C. has D. he
56. There was ____ to prevent the accident.
A. something could do B. anything we could do
C. nothing we couldn't do D. nothing we could do 《高中英语语法-定语从句》由英语我整理,更多请访问:s://.liuxue86/english/
什么叫复合不定代词
#英语# 导语代词是代替名词以及起名词作用的短语、不定式、动词的-ing形式、从句或句子的词。在英语中代词用得极为广泛。正确地运用代词可以使句子简洁、明快,但如果使用不得当也容易产生意义理解上的偏差。英语中的代词分为九类:人称代词、物主代词、反身代词、指示代词、相互代词、疑问代词、不定代词、关系代词和连接代词。
1.人称代词概述
人称代词是表示“我(们)”、“你(们)”、“他(们)”、“它(们)”的词。人称代词不仅指人,也可指物,有人称、数和格的变化。人称代词有主格和宾格之分,主格形式在句中作主语、表语等成分;宾格形式在句中作动词宾语、介词宾语、同位语等,有时也作表语。
(1)单数:
①主格:
第一人称(I)
第二人称(you)
第三人称(he,she,it)
②宾格:
第一人称(me)
第二人称(you)
第三人称(him,her,it)
(2)复数:
①主格:
第一人称(we)
第二人称(you)
第三人称(they)
②宾格:
第一人称(us)
第二人称(you)
第三人称(them)
I chose Mary,but she didn‘t agree to go with me.(she为主格作主语,me为宾语作介词with的宾语。)
我选择了玛丽,可她不愿和我一起去。
I love swimming.It keeps me fit.(it在句中作主语。)
我喜欢游泳,它可以使我保持健康。
—Who took away all the books here?
—It‘s I/me.(I/me作表语,在口语中作表语常用宾格。)
—谁把这里的书都拿走了?
—是我。
We,us three will be able to fulfil the task.(us作we的同位语)
我们,就我们三人能出色完成这项任务。
Me believe you!(宾格形式在口语中表示强调时,偶尔也可作主语。)
我相信你!
2.人称代词的用法
(1)主格I在句中的任何位置都必须大写。
(2)在英语中如果出现多个人称代词,如果是单数并列需要按照“你”、“他/她”、“我”的顺序排列;复数并列则按照“我们”、“你们”、“他们”的顺序排列,即单数并列为you,he/she(him/her)and I(me);you and I(me);复数并列为we(us),you and they(them)。如果是承担责任,说话者则把I(me)或we(us)放在第一位。
You,she and I should work together and play together.
我、你和她应当共同工作、一起玩。
I and Li Ming broke the window.
我和李明把窗户打碎了。
(3)it有时可指不知性别的“婴儿或小孩”或对人物身份进行断定。
The baby is crying.It must be hungry.
婴儿在哭,他/她准饿了。
—Who is standing at the back?—It must be Laura.
—是谁站在后面的?—准是劳拉。
(4)人称代词用于as和than之后,如果as和than看作介词,此时往往用宾格;如果是连词,则往往用主格。
She speaks Japanese as well as me/I.(此时口语中常用me。)
She speaks Japanese as well as I do.(此时把as作为连词。)
她日语说得和我一样好。
(5)人称代词单独使用时,常用宾格而不是主格。
—I‘d like to stay here for another week.
—Me too.
—我还想再在这里呆一周。
—我也是。
—You are supposed to help Jack.
—Why me?
—你应该帮助杰克。
—为什么是我帮助他?
3.人称代词的特殊用法
(1)it的详细用法请参阅第二部分第6章“It的用法”。
(2)we,you,they的特殊用法
在英语中we,you和they都可泛指人们,可译为“我们”、“你们”、“他们”。
We all get into trouble sometimes.(we泛指人们)
我们每个人有时都会遇到麻烦。
They say that everyone can make mistakes.(they泛指人们)
人们说每个人都会犯错误的。
You should do your best at all times.(you泛指人们)
无论何时人们都应尽的努力。
(3)she,he等的特殊用法
①she可以用来代表国家、船只、大地、月亮等。
China will always do what she has promised to do.(代指国家)
中国总会按照自己的去做任何事情的。
Titanic was the greatest boat of the time but she sunk down to the bottom of the Atlantic Ocean.(代指船只)
泰坦尼克号是当时的船,可它沉到大西洋的海底了。
②男主人常用she/her代指自己的爱车、宠物等。
Would you please take care of my little parrot?She needs good care.(代指鹦鹉)
你能不能照顾一下我的鹦鹉?她需要好好照顾。
—Your car looks smart.When did you buy it?
—I bought her a week ago.(代指车)
—你的车样子真好。什么时候买的?
—一周前买的。
③女主人常用he/his代指自己的车、宠物等。
My car still runs perfectly.He has been working for me a dozen years.(He代指the car)
我的车依然运转很好,他为我工作已12年了。
④在寓言、故事中,温柔、善良的动物(鹿、猫、熊猫、小鸟等)常用she替代,凶猛、粗野的动物(老虎、狮子、狼、熊、狐狸等)常用he替代。
Panda Lily is a new member of the circus.She needs time to get used to the new life.(She替代Panda Lily)
熊猫丽丽是马戏团的新成员。她需要时间适应新的生活。
The fierce tiger came at the monkey when the monkey escaped him into the thick trees.(him代指the tiger)
凶猛的老虎向猴子扑来,而猴子逃到茂密的树林里去了。
高考英语语法填空的技巧和方法
'Someone'/'somebody','anyone'/'anybody'and'no one'/'nobody'are indefinite pronouns.They refer to people.We use them when we do not know or do not need to mention by name who we are talking about.
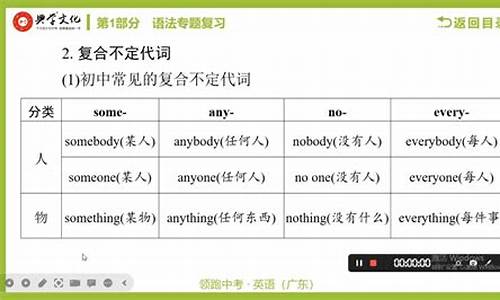
1. some, any, every, no都能和one, body, thing一起构成代词,这些代词叫复合不定代词。它们基本含义为:
指
人 somebody
someone 某人 anybody
anyone
任何人 everybody
everyone每人 nobody
no one
没人
指物 Something某物某事 anything任何事物 everything一切 nothing没东西
2. 一般情况下,some构成的复合不定代词,其作用和some相同,用于肯定句;any构成的复合不定代词用于否定句或疑问句;no构成的复合不定代词表示否定含义,用于否定句。如:
① I he something to tell you. 我有事要告诉你。
② He didn’t say anything at the meeting yesterday. 昨天在会上他没发言。
③ Everybody likes swimming. 每个人都喜欢游泳。
④ There is nothing wrong with your ears.
你耳朵没毛病。
3. something可用于提建议或请求的问句中,以及希望说话对方作出肯定回答的问句中。如:
Would you like something to eat? 你要吃点东西吗?
4. 复合不定代词在句子中作主语时,谓语动词一般用单数形式。如:
Nobody knows his name. 没有人知道他的名字。
5. 不定代词的定语要后置。如:
Is there anything important in today’s newspaper? 今天的报纸上有什么重要新闻吗?
一般的,不定代词(包括复合不定代词)在句子中,通常用三单形式
复合不定代词即由some,any,no,every加body,thing,one构成,用来表示一个全部概念,分别表示人或物。在句子中可作主语、宾语、表语。由于用法上的习惯常为高考所青睐,下面就其常见考点分析如下:
一、与部分否定结下了深厚的情谊
部分否定是高考常考考点之一,常表达为:not+全部肯定词或全部肯定词+not,其意义为“并非都,不都”。前者为基本概念,通常,学生有一定的掌握;但后者与一般否定句相似,易引起学生判断上的失误,也是作者出题,命题的焦点。uniwant
1.I agree with most of what you said,but I don't agree with____.
A.everything D.anything
C.something D.nothing
2.—The exam was difficult,wasn't it?
—No,but I don't think____could pass it.
A.somebody B.anybody
C.nobody D.everyboby
分析:1,A.由句意“我同意你说的大部分,而不是全部”,可看出后面表示部分否定,构成not…everything,即“并非每件事”。2,D.同理,“并非所有人都能通过”,部分否定概念,构成not…everybody,即“并非所有的人”,本题还应考虑否定转移。以上两题要求学生在作题时认真审题,仔细品味作者在题干中蕴涵的逻辑关系,灵活应用所学知识,取得满意效果。
二、在反意问句中考查对应的主语
反意疑问句在确定主语时,常被列为考点。当主语为表示人的复合不定代词时,疑问部分的主语常用they(有时也用he);当主语为表物的复合不定代词时,疑问部分的主语通常为it。
1.Nobody wants to waste time watching boring plays,____?
A.does it B.do they
C.is he D.are they
2.I am sure everything goes well,____?
A.doesn't it B.does they
C.doesn't everything D.aren't I
分析:1,B.句子主语为指人的复合不定代词,对应的主语是they,又为否定句,故选B。2,A.I'm sure为插入语,句子主语为指物的复合不定代词,对应的主语是it,故选A。通过以上两题分析,要求学生思路清晰,运用所学知识,具体问题具体分析。
三、和定语从句也保持着一定的联系
指人、指物的复合不定代词常与定语从句结合考查,其重点在连接词选择问题上。当先行词为指物的不定代词时,关系代词为that,但something例外,既可用that也可用which。当先行词为指人的复合不定代词时,关系代词为who或that。注意作宾语的关系代词省略也是考查的重点。
1.Finally,the thief handed everything____he had stolen to the police.
A.which B.what
C.whatever D.that
2.____breaks the rule should be punished.
A.Those who B.Who
C.Anyone who D.The one
3.Now let's think of feedback as something____·
A.that we should make to work for us
B.we should make work for us
C.in which we should make work for us
D.we should make work for us in
分析:1,D.先行词everything,在定语从句中作stolen宾语。2,C.由定语从句谓语即可确定。3,B.先行词something在定语从句中作make宾语,省去了关系代词。以上试题可看出知识之间环环相扣,体现了高考试题中多元结构的考查。
四、复合不定代词的定语位置
修饰复合不定代词的形容词一般后置。注意它常与其它考点联系起来考查,看下面练习。
1.There is____in today's newspaper.
A.nothing specially interesting
B.specially interesting nothing
C. nothing specially intertesting
D.intertesting specially nothing
2.He asked me if there was____to read.
A.easy enough something
B.enough easy something
C.something easy enough
D.something enough easy
分析:1,A.interesting修饰nothing放其后,specially副词修饰形容词interesting。2,C.easy修饰something放其后,副词enough修饰easy,放其后。以上两题要求认真分析,弄清英语词序间修饰关系。
五、复合不定代词常用于简略回答中
一般情况下,用nothing回答以what开头的问句;nobody(no one)回答who开头的问句。
1.What's on the blackboard?
—Nothing.
2.—Who's in the classroom?
—Nobody(No one).
六、复合不定代词的一致问题
复合不定代词作主语,谓语动词用单数。
Everything is not in good order but at sixes and sevens.
Nothing except for a few books was left for him by his father.
七、复合不定代词间的用法区别
1.带some的复合不定代词,一般用于肯定句;而带any的复合不定代词常用于否定句、疑问句和条件句中。
I he something important to tell you.
If there is anything the matter with the machine,please let me know.
2.带some的复合不定代词,用于疑问句,表示说话人希望得到肯定回答或表请求、建议、征询意见的句子中。
—Is____here?
—No.Bob and Tim he asked for lee.
A anybody B somebody C everybody D nobody 选C。
3.带any的复合不定代词,用于肯定句中,表示“任何人,任何事”。
Anyone who refused to bow was thrown intoprison.
As a teacher,I would do anything for my students.
4.带any的复合不定代词作主语,其后不能再用否定式,要表达否定概念,需用相对应的全部否定意义的词。
Anything could not be seen in that dark room.(×)
Anything could be seen in that dark room.(√)
5.指人的复合不定代词合写与分写,其意义与用法不同,以any为例:
anyone 仅指人 任何人,某人 不与of短语连用
anyone指人又指物 任何一个 可与of短语连用
Anyone can do the job.
Any one of us can do the job.
八、复合不定代词常见短语
1.he something to do with
与……有关
2.something like
几分像,大约
3.something of
在某种意义(程度)上
4.anything but
除……外任何,根本不……
5.anything like
像那样的事,全然不
6.anything of
一点儿,一点……味儿
7.he nothing to do with
与……无关,和……不往来
8.be nothing to
对……无足轻重,不能与……相比
9.to say nothing of
更不必说
10.for nothing
免费,徒然,没有理由
11.all to nothing
百分之百的
12.nothing but
除……以外什么也不,只有
九、复合不定代词在谚语中应用
1.Everybody's business is nobody's buslness.
都管等于没人管。
2.Everybody's friend is everybody's fool.
每人的朋友是每人的傻瓜。
3.Everytking is good for something.
凡物都有用。
4.Everything has two sides.
事物都有两个方面。
5.The man who is everything is nothing.
什么都是的人什么都不是。
6.He who has no conscience has nothing.
没有良心的人一无所有。
7.Nothing succecds like success.
一事成功,事事顺利。
8.Nothing venture,nothing he.
不入虎穴,焉得虎子。
9.Money isn't everything.金钱不是万能的。
10.To know everything is to know nothing.
样样皆通,样样稀松。
11.Everything is good when new,but friends when old.东西是新的好,朋友是老的好。
十、智能转化
1.He often asked the questions that____his lesson.So he was often scolded by his teacher.
A.had something to do with
B.was separated from
C.was connected with
D.had nothing to do with
2.—This car is worth 90,000 dollars.
—Oh,I care more about quality,you know,money is____to me.
A.nothing B.anything
C.everything D.something
3.—Nowadays an unexpected thing is possible to hen.
—Yes, everything strange is____strange.
A.something B.anything
C.everything D.nothing
4.—What an amazing film!It's the most interesting film I've ever seen.
—But I'm sure it won't interest____.
A.somebody B.anybody
C.everybody D.nobody
5.The book is of good value.____can be enjoyed from it until you he a deep understanding of it.
A.Something B.Nothing
C.Much D.Few
6.He who is proud of his wealth has rarely____else to be proud.
A.anything B.something
C.everything D.nothing
7.His theory is much more important than____.
A.any of us B.any of our
C.anyone else's D.anyone's else
8.He cares so little about his meals that____will do so long as it fills his stomach.
A.anything B.everything
C.nothing D.something
9.It was such a tiny village that____knew____else well.
A.anybody,somebody
B.everybody,everybody
C.anybody,anybody
D.nobody,nobody
10.I tried____but there was no result.
A.everyone B.every one of them
C.everyone of them D.every of them
11.I'll never know what was on his mind at the time,nor will.____(04江苏)
A.anyone B.anyone else
C.no one D.no one else
12.Playing tricks on others is____we should never do.(04湖南)
A.anything B.something
C.everything D.nothing
13.I'm,just as is sung in a song,____I live on my own.
A.someone B.somebody
C.anybody D.nobody
14.—Do you mind if you give Tom a hand?
—Yes,I do.I'll be glad to help____Tom.
A.anybody but B.somebody but
C.everybody but D.nobody but
15.The fellow was said to be____of a scholar.As it turned out,he was a cheat.
A.everything B.much
C.something D. nothing
16.—What is the man,actually?
——I don't know for sure.But I think he can be____but a teacher.
A.something B.anything
C.nobody D.anyone
参考答案:
1-5 D A D C B 6-10 A C A C B
11-15 B B D A C 16 B
-
英语中的代词是什么意思
具体解析语法填空技巧
技巧一:名词形式变化。名词的形式变化主要有单数、复数、所有格的变化。
技巧二:动词形式变化。动词的形式变化比较多,有谓语的变化(时态、语态、语气),有非谓语的变化(不定式、动名词、现在分词、过去分词)。
技巧三:代词形式变化。代词形式变化通常是与人称变化有关。即人称代词(主格和宾格)、物主代词(形容词性和名词性)、反身代词。还有几个不定代词的形式变化,如no one/none、other/another。指示代词(it 和this)it 用作引导词等。
技巧四:形容词、副词比较级变化。英语中大部分形容词和表方式的副词都有原级、比较级和最高级的变化。构成比较级和最高级的方式,或通过加后缀-er 和-est,或在词前加more/less 和most/least,且形容词的绝对最高级还要冠以the。
技巧五:数词形式变化。数词的形式变化包括基数词、序数词,或加后缀-、-ty 的变化,甚至还有作分母用的序数词的单复数形式,以及one/two 的特殊变化形式once/twice。
技巧六:词的派生。词的派生现象在英语单词中是很常见的,派生现象主要发生在名词、动词、形容词、副词四种词中。这种题型还有可能检测学生对词根、前后缀、派生词的掌握。
技巧七:固定短语结构。根据句中横线前后及整句来判断横线前后是否构成一个固定短语,但有时要对横线前或后的几个单词结合看才能命中答案。
技巧八:从句引导词。从句是此题型最为常见的一个方向,主要考查学生对各种从句掌握程度。
技巧九:短语动词结构。短语动词是以动词为中心的两个或多个词构成的短语,此类短语中往往是动词与介词或副词连用的多些。
技巧十:介词、短语介词结构。常用的介词有in,at,on,before,during 等,通常考查固定搭配。短语介词即多个词的组合起介词作用的短语,如:except for,due to 等。
技巧十一:连词、关联短语结构。常用的连词有and,or,but,so,for,while 等,常用的关联短语both……and,either……or,neither……nor,not only……but also 等。
技巧十二:冠词无提示词名词之前。冠词只能是在a,an,the之间判断。
技巧十三:上下文中出现的相关词。这是较难的,但也是通过上下文去做题时最有效的方法。学生可以根据上下文关系和自己积累的知识,填入某个词。
语法填空无提示词可以填不定代词吗
代词是代替名词及起名词作用的短语或句子的词。
代词的用法:
1.可分为人称代词、物主代词、指示代词、相互代词、疑问代词、连接代词、关系代词、不定代词等九类。
2.人称代词有主格和宾语之分:主格用作主语,宾语用作宾语。但在口语中,当人称代词用作表语,用于than, as 之后或用于强调句中被强调时,用主格和宾格均可以。
3.物主代词分形容词性物主代词和名词性物主代词。形容词性物主代词在句中只用作定语;名词性物主代词则不能用作定语,但可以用作主语、宾语、表语、连用of作定语等。
高中英语语法知识点整理总结
可以。
不提供单词的填空只考以下四种词∶包括人称代词,物主代词,指示代词,不定代词。
特别留意the常用的场合,包括最高级,序数词前面等,连词∶包括并列连词及各种从句中的引导词。其中,定语从句及名词性从句中的同位语从句是高考热点。
代词的固定搭配
高中英语知识点有哪些?应该怎么学习高中英语?有很多的同学是非常想知道,高中英语语法知识点有哪些,我整理了相关信息,希望会对大家有所帮助!
↓↓↓点击获取更多"高中英语知识点"↓↓↓
★ 高一英语必修一语法知识 ★
★ 高考英语作文万能句子 ★
★? 高三英语复习范文 ? ★
★ 英语作文热点话题及范文 ★
高中英语语法重要知识点 :不定冠词
不定冠词a,an与one同源,表示微弱的一的概念,但并不强调数目,用来表示不确定的人或事物。
A用在辅音前,而不是辅音字母前;an用在元音前,而不是元音字母前。
a university in Asia
1.表示同类中的任何一个
A cat has nine lives.
2.表示泛指的某人、某物
I know a John Lennon,but not the famous one.
3.表示数量的
He has a daughter.
4. 表示单位数量的每一
I earn 10 dollars an hour.
5.表示相同的
The two birds are of a color.
6. 用于集体名词前
He grows up in a large family.
7. 在某种情况下可用于抽象名词和物质名词前
China has a long history.
高中英语语法知识点整理 总结 : 定冠词的用法
1.表示特定的人或物
2.表示地球、宇宙中独一无二的事物
主要指各种天体及世界上比较有影响的物体。The sun,the moon,the earth
3.表示地点、方向、时间、方式等 at the corner 在拐角处
1) 在表示季节的名词前常不用冠词。In spring 在春天
2) 具体某年的某个季节,需用冠词。In the summer of the year2008
3)用于序数词或形容词的最高级前 the first the second
4)用于形容词前使其名词化 the rich the poor
5)用于复数姓氏前,表示―夫妇‖或全家 The Smiths
6)用于乐器名词前 Play the piano
7)用于by+the+计量单位名词 By the pound
1. 用于复数名词前
复数名词泛指某类人或物时,其前通常用零冠词。Students should obey the school rules. 学生应该遵守校规。复数名词若需特指,则要加定冠词。The students are too lazy. 这些学生太懒。
2. 用于不可数名词前
不可数名词表示泛指时,其前通常用零冠词。如:Bread is made from flour. 面包是用面粉做的。
Wood is a poor conductor of sound. 木头是声音的不良导体。不可数名词若需特指,则要加定冠词。
He sawed the wood into three pieces. 他把木头锯成三块。
3.用于专有名词前
在通常情况下,专有名词前要用零冠词。如:
Mr Smith is our English teaches us English. 史密斯先生教我们英语。在特殊情况下,若专有名词需要特指,也可加定冠词。如:The Smith you‘re looking for no longer lives here.
4. 用于抽象化的可数名词前
有些可数名词抽象化后表示表示的活动,其前通常零冠词。Jim has gone to bed. 吉姆已上床睡觉了。
She goes to church every Sunday. 她每周星期天都去做礼拜。
这类主要涉及bed, church, class, college, school, university, work, hospital, prison, market, sea, town等。另外,这类名词前用不用冠词有时与英美英语的表达习惯有关。如:―住院‖在英国英语中通常说成 in hospital,而在美国英语中则通常说成in the hospital;类似的还有go to university (英)上大学 / go to the university (美)上大学;at table (英)在吃饭 / at the table (美)在吃饭。
5. 用于职务及头衔前
当表示职务及头衔的名词用作表语、补足语及同位语时,其前通常用零冠词。如:Wilson became President of the U. S. A. 威尔逊当了。He will be made captain of the football team. 他将被选为 足球 队队长。
6. 在表示学科、语言、三餐、月份、季节、节日、星期等名词前,通常用零冠词。
We are all interested in physics. 我们大家都对物理感兴趣。
7. 用于某些固定结构中
go to sea 去当水手 at home 在家 at night 在晚上 at least 至少
at most 至多 at first 首先 at last 最后 in bed 在床上
on foot 步行 face to face 面对面
高中英语语法知识点整理总结:代词
高考中对代词的考查主要集中在人称代词(主要是其中的it)、关系代词、指示代词和不定代词上。
一、 it的用法 ?
1.作人称代词
John likes playing Ping pong./ He always does it in the afternoon.(指代上下文提到的事物); /It's time we went home. / How far is it from here to your home ? / It is getting warmer and warmer./ It's very quiet at the moment.(可指时间、天气、环境等) 2.引导词
A.作形式主语,代替由不定式、动名词或从句表示的真正主语。
It's important for us to learn a second language./ It's no use talking to him./ It's known to all that the earth goes round the sun.
B.作形式宾语,代替由不定式、动名词或从句表示的真正宾语。
We feel it our duty to help others./ He made it clear that he would lee the city. C.强调结构:It is (was) +被强调部分+that (或who)…
注意:在强调结构中,如被强调部分为时间状语或地点状语,其后的连接词也绝不能为when 或where,而应用that 。在复习中,一定要注意句式的不同。It was in Shanghai that I bought the guitar.(that引起强调句) It was Shanghai where I bought the guitar.(where引起定从)
It was twelve o'clock when we arrived there.(when引起时间状语从句) It was at twelve o'clock that we arrived there.(that 引起强调句)
3. it,one,that 的区别:作为代词,这三个词的对比使用是高考的 热点 之一。—Why don't we take a little break? —Didn't we just he __________? A.it B.that C.one D.this
The Parkers bought a new house but _________will need a lot of work before they can move in. A.they B.it C.one D.which
one 用以指代同类事物中的任一,that 特指性强,指代可数与不可数词,而it指代上文提过的同一事物。
二、 关系代词
who,whose,whom,which,that,as
1)which可以引导非限定性定语从句,代表前面整个 句子 的内容,并且在从句中做主语 2)that的用法 1)不用that的情况
a) 在引导非限定性定语从句时。b) 介词后不能用。
We depend on the land from which we get our food. We depend on the land that/which we get our food from.
2) 只能用that作为定语从句的关系代词的情况 a) 在there be 句型中,只用that,不用which。
b) 在不定代词,如:anything, nothing, the one, all, much, few, any, little等作先行词时,只用that,不用which。
c) 先行词有the only, the very修饰时,只用that。d) 先行词为序数词、数词、形容词最高级时,只用that。. e) 先行词既有人,又有物时。
举例:
All that is needed is a supply of oil. 所需的只是供油问题。
Finally, the thief handed everything that he had stolen to the police. 那贼最终把偷的全部东西交给了警察。
3) as的用法
AS作关系代词,用来引导定语从句:限制性定语从句和限非制性定语从句 一、AS引导限制性定语从句
AS引导限制性定语从句时,通常和such, the same, as(so)等连用,构成such...as/such as, the same...as/the same as, as(so)...as等结构,在从句中可作主语,宾语和表语。
1.such...as/such as意为―...的那种...,像那样的‖,such...as/such as引导限制性定语从句时,既可指人,也可指物。such用于名词之前时,具有形容词性质;such单独使用(即后面不接名词)时,具有代词性质。
Don‘t trust such men as praise you to your face.(as作主语) 不要相信那种当面吹捧你的人。
You should read only such books as you can understand without much difficulty.(as作宾语) 你应当只读那些你读起来不太难懂的书。
Associate with such as will improve your manners.(as作主语) 要和能改善你的言行的那种人结交。
2.the same...as/the same as意为―与...同样的‖,和such一样,the same既有形容词作用,又有代词性质。
We he arrived at the same conclusion as they he.(as作宾语) 我们已得出和他们同样的结论。
比较:the same...as和the same...that不同,前者是―同那一个相似‖,后者是―正是那一个‖。如:
This is the same watch as I lost. 这同我丢的那块表一样。
This is the same watch that I lost? 这正是我丢的那块表。
3.as(so)...as意为―和...一样‖,后接由many, much等修饰的名词或由形容词修饰的单数名词,注意其语序为as(so)+adj.+a+n+as,如:It‘s as pleasant a film as I he ever seen. 这是一部和我以往看的同样好的**。
As many soldiers as marched were killed. 很多游行的战士都被杀了。
注意:such ...as与such...that ,so...as与 so...that的区别:that是连词,引出结果状语从句,在从句部分不作成分;as是关系代词,引出定语从句,在从句中可作主语,宾语和表语。比较:He is such a nice boy that everyone likes him. He is such a nice boy as everyone likes.
It is so difficult a problem that nobody can work it out. It is so difficult a problem as nobody can workout.
三、AS引导非限制性定语从句
AS引导非限制性定语从句时,通常指的不是主句中的某一个名词(先行词),而是指整个主句表达的内容,对主句所作的陈述进行附加说明,意为―这...,如...或正如...‖。这种从句可位于主句之前,之中或之后。
As we all know, Taiwan belongs to China. Taiwan, as we all know, belongs to China. Taiwan belongs to China, as we all know. 注意下面的习惯用法:
as is well discussed 正如已讨论过的
as is often said 正如通常所说 as is often the case 通常就是这样 as has been pointed 正如所指出的那样 as has been said before 如上所述 as often hens 如同经常所发生的那样 as might be expected正如所料 as is well known to all众所周知
在多数情况下,从句中的谓语助动词可以省略 as explained before 如前面所解释的 as mentioned above 如前面所提到的 as shown in the figure 如图所示 as seen from the table 从表中可以看出 as already discussed 正如已讨论过的
四、不定代词
一) . some 与 any 的用法
1. some 用于肯定句以及表示建议或期待得到肯定回答的问句。修饰单数名词时,意为某个。如:
I he some questions about the assignment. (希望得到肯定答复)。
2. any 用于否定句和疑问句时,表示一些。用于肯定句时,只和单数名词或不可数名词连用,表示任何。如:
The medicine is on sale every where. You can get it at any chemist?s. 二) . each 与 every 的用法
1. each 强调个体,表示两个或两个以上中的每一个,在句中可充当主语、宾语、定语和同位语。如:
There are trees and flowers at each side of the road.
2. every 强调整体,表示三者或三者以上中的每一个,只能作定语,不能说 every of them ,要说 every one of them .
Every student in our class works hard. 三 . no one 与 none 的用法
1. no one 意为没有人,只能指人,不能指物,不可与介词 of 连用,谓语动词用单数形式,回答 who 引导的问句。如:Who is in the classroom? No one.
2. none 既可指人,也可指物,强调数量,意为一点也不,一个也不;谓语动词既可用单数也可用复数;常与 of 连用,通常指三者以上的人或物中没有一个,回答 how much 和 how many 引导的问句。如:
They were all tired, but none of them would stop to he a rest. 四 . other, another, others, any other, the other 的用法
1. other 表示泛指,意为另外的、 其它 的。常与复数名词或不可数名词连用。如果其前有 the, this, some, any, each, every, no, one 以及形容词性物主代词时,其后就可接单数名词。如:I he no other place to go.
2. another 常用于指三者或三者以上中的另外一个,泛指单数。可单独使用,也可后接名词。如果其后接复数名词,则表示又、再、还。如:This cap is too small for me. Show me another (one)。We need another three assistants in our shop.
3. others :它是 other 的复数形式,表示泛指,意为别的人或物,但不指全部。特指时在其前加定冠词;前面可加任何限定词以及数量词。如:He has more concern for others than for himself.
4. any other 表示一个之外的其他任何一个,而不是两个之中的另一个。如:China is larger than any other country in Asia.
5. the other :表示两者中的另外一个。可单独使用,也可接单数名词。如:No agreement was reached in the discussion as neither side would give way to the other.
五 . all 与 both 的用法 均表示都,但 all 表示三者以上的人或物, both 则表示两个人或物。二者都表示肯定意义,如果与 not 连用时,则表示部分否定。
六 . neither 与 either 的用法 都可用于表示两个人或物。neither 表否定意义,意为(两者中的每一个)都不;而 either 表肯定意义,意为(两者中的每一个)都。都可单独使用,也可同介词 of 连用。如:Both teams were in hard training; neither willing to lose the game. Do you want tea or coffee? Either. I really don't mind.
高中英语语法的 学习 方法
首先先你要端正心态,不要急躁,,你做你自己的事,这样才能静下心来学习。要成为英语高手就必须比别人走更多的路,做更多的事。你应该明白一个事实,英语是单词和语法的综合,所以单词和语法都要拿下。
其次,对于单词,有如下几种方法,第一个,是加强记忆的频度,也就是说,早上记了几个,隔几个小时又看一次,总之一天之内,记忆的间隔不要太长,否则你辛苦积累的记忆会随着时间的延长而淡化,第二个,是可以根据自己的理解编 顺口溜 ,比如good morning 是狗摸你…(见笑了)…,第三个,最重要的是,记单词的时候,不要忘了阅读,一边记单词,一边看 文章 ,这样可以把孤立的单词串联起来,记忆的效果会加倍,第四个。
我建议你记单词要分门别类记忆,要形成一个意群,比如,重要性用magnitude magnificence ,表示非常,大大地有exceedingly,tremendously,extremely……这样做在你写作时,是十分有好处的,写作时不要尽写一些低级词汇,你要写高级词汇,比如重要性写magnitude,许多写a multitude of 或者handsome。
高中英语语法知识点整理总结相关文章:
★ 高中英语语法归纳整理
★ 高中英语语法总结
★ 高中英语语法归纳总结
★ 高一英语语法知识点总结
★ 高一英语语法知识点总结(2)
★ 高二英语语法知识点
★ 高三英语的语法知识点归纳
★ 高中英语的语法知识总结
★ 高中英语的知识点归纳
★ 高中必备英语知识点归纳
var _hmt = _hmt || []; (function() { var hm = document.createElement("script"); hm.src = "s://hm.baidu/hm.js?fff14745aca9358ff875ff9aca1296b3"; var s = document.getElementsByTagName("script")[0]; s.parentNode.insertBefore(hm, s); })();英语代词的用法全归纳
一、定义与分类
代词是代替名词及起名词作用的短语或句子的词。代词根据其意思和用法可分为人称代词、物主代词、反身代词、指示代词、相互代词、疑问代词、连接代词、关系代词、不定代词九类。综观历年高考情况,在这九类代词中,不定代词一直是高考英语的重点。
二:人称代词,物主代词,反身代词用法概述
这三种代词都有人称(一、二、三人称)的变化、数(单、复数)的变化,以及性(阴性、阳性、中性)的变化。其中,人称代词除了这三种变化外,还有格(主格、宾格)的变化。
物主代词又包括两种形式:形容词性物主代词和名词性物主代词。特别注意:形容词性物主代词its没有相应的名词性物主代词。
这三种代词的形式变化表如下:
三、人称代词的用法
1) 定义:人称代词是用来指代人、动物或事物的代词。它必须在人称(第一人称、第二人称、及第三人称)、数(单数、复数)以及性(阴性、阳性、中性)三方面与被指代的名词一致。代词一致。
如:I am a student. Tom is a boy, and he is a student.
Mary is very pretty, and she likes singing.
The boys are students, and they are in the room.
The doy is small. It is Tom's.
2) 人称代词的句法功能
A) 人称代词有主格和宾语之分:主格用作主语,宾格用作宾语。宾语一般在Vt.和Prep.后。
B) 人称代词的主格形式在在句中作主语和表语。 做主语时,人称为二三一。但是复数形式时为一二三。注意主谓一致:第三人称。
如: I like music(主语).
She is a teacher.(主语)
You,he and I are good friends(主语).
Neither she nor I am student. It might he been she.
C) 人称代词的宾格在句子作动词的宾语,或者介词的宾语。
如:I saw him at the party(宾语).
I bought a book for them.(作介词宾语)
=I bought them a book.(间接宾语)









